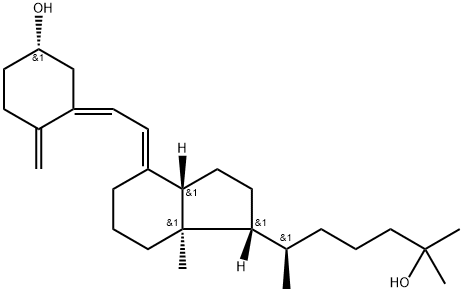
Chemical Name: Calcifediol
CAS No.: 19356-17-3
Molecular Formula: C27H44O2
Molecular Weight: 400.65
Calcifediol CAS 19356-17-3
Description
Calcifediol Quick Details
Chemical Name: Calcifediol
CAS No.: 19356-17-3
Molecular Formula: C27H44O2
Chemical Structure:
Molecular Weight: 400.65
| CALCIFEDIOL Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 74-76oC |
| Boiling point | 529.2±33.0 °C(Predicted) |
| density | 1.01±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Fp | 14 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 20 mg/ml; DMSO: 10 mg/ml; Ethanol: 20 mg/ml; Ethanol:PBS (pH 7.2)(1:2): 0.3 mg/ml |
| pka | 14.74±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | White to off-white crystalline solid. |
| color | White to off-white |
| biological source | synthetic |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive, Temperature Sensitive |
| InChIKey | JWUBBDSIWDLEOM-DTOXIADCSA-N |
| SMILES | C[C@]12CCC/C(=C\C=C3\C[C@@H](O)CCC\3=C)/[C@]1([H])CC[C@]2([H])[C@H](C)CCCC(O)(C)C |&1:1,10,16,20,22,r| |
CALCIFEDIOL Chemical Properties,Uses
Description
Calcifediol (synonym 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3) is a vitamin D analog and the major metabolite of vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) in the liver. Its main function is the regulation of calcium and phosphorus, which is necessary for strong bones. It is used to treat patients with serious kidney diseases to decrease the parathyroid hormone (PTH) level. It is used to treat rickets and osteomalacia, both in azotemic and non-azotemic patient.
Therapeutic drug for bone disease
The natural source of Vitamin D in the body depends on ultraviolet rays of sunlight, making the 7-dehydrocholesterol convert into vitamin D3, at first under the action of vitamin D3 hydroxylase in liver vitamin D3 converts into the Calcifediol, vitamin D3 mainly is present in the form of the Calcifediol in the blood, in the kidney the Calcifediol is further converted to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol for short) and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, activity of calcitriol is 2-5 times of the Calcifediol, the two drugs can promote bone re-absorption of calcium and intestinal absorption of Ca2 +. In addition to regulating the body’s calcium and phosphorus metabolism, this product can promote the intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus, promote calcium and phosphorus deposits in the bone tissue, promote bone formation.
Calcifediol itself has a certain activity, can be used for the treatment of metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis, rickets, osteomalacia, but also for hemodialysis-induced hypocalcemia. Patients with chronic renal failure combined with metabolic bone diseases, engaged during dialysis, can be applied. It can increase the levels of serum calcium, can reduce levels of serum alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone, improve radiological and histological sign of osteitis (with or without osteomalacia). Bone resorption, hyperparathyroidism and osteodystrophy signs of mineralization defects all can be reduced, as for osteomalacia patients and children who are unable to obtain sufficient bone development because of renal osteodystrophy or parathyroid dysfunction, may be more favorable than calcitriol. Such cases can be treated with Calcifediol and calcitriol. But as for osteomalacia accompanied by gastrointestinal diseases, Calcifediol is preferable. If because of liver disease to cause generated obstacles of 25-OHD in vivo, secondary osteomalacia, can also try to use this product. But osteomalacia caused by aluminum poisoning, treatment of vitamin D preparations often is ineffective. Chelator deferoxamine (Desferal) clear aluminum of blood dialysis, can be effective.
Osteomalacia and rickets (in children causing deformities severe osteomalacia) is characterized by obstacle of bone mineralization and non-calcified bone-like tissue or cartilage accumulation. Bone changes of Vitamin D-related bone softening, accompanied with normal or reduced levels of serum calcium and phosphorus, increased serum alkaline phosphatase, and PTH is secondary increased.
Osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone tissue thereby increasing the likelihood of fractures. Pathological mechanism may be an increased rate of bone resorption, exceeding bone formation; or decreased bone formation, and bone resorption is also still normal or reduced. Bone is progressive missing, can compress and collapse the spine, causing pain, body shorter and kyphosis. Patients are also prone to the outer periphery fracture.
Side effects and precautions
Like all the vitamin D metabolites, excessive Calcifediol can also cause increased serum calcium, in urine can increase high. Therefore, in the dose adjustment period, serum calcium should be monitored at least once a week, if increased serum calcium was found, it should be discontinued.
Pregnant women use this product, there is no adequately controlled studies, but in experimental animals, teratogenic effects have been found.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classify the product into pregnancy category C drugs.
People who use digitalis, should be used with caution vitamin D, because increased calcium may induce arrhythmia.
Other side effects and precautions, see “Vitamin D2” (Vita-min D2) that is ergocalciferol.
Action of Vitamin D2 is intense, may cause damage. Increased serum calcium caused by excess, can cause gastrointestinal and central nervous system lesions, soft tissue calcification. Kidney complications can be very serious and even cause death. Such as increased serum calcium persists, after discontinuation, kidney damage likely will continue for a long time. An individual who the amount is not too large, but also because of increased sensitivity to occur adverse reactions.
Calcifediol is rapidly absorbed, at 4 to 8 hours up to serum peak concentration. Transport shall bind with protein, half-life is about 16 days.
Uses
- 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-23,24,25,26,27-13C5can be used as a stable isotope internal standard for data interpretation in specific biological samples by mass spectrometry.
- A metabolite of Vitamin D. The principal circulating form of vitamin D3, formed in the liver by hydroxylation at C-25. Calcium regulator.
- This product may be used as an analytical standard.
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxycalciol that is calciol in which the hydrogen at position 25 has been replaced by a hydroxy group. A prehormone resulting from the oxidation of calciol in the liver, it is further hydroxylated in the kidney to give calcitriol, the active form of v tamin D3.
Therapeutic Function
Calcium regulator
General Description
25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is a prohormone produced via hydroxylation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) in the liver. It is a precursor for the synthesis of calcitriol {1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 or [1,25(OH)2D3]}. It is used as a biomarker to determine the status of vitamin D in the body.
25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-23,24,25,26,27-13C5?is an isotope of vitamin D3 wherein C-23, C-24, C-25, C-26, C-27 carbons are replaced by 13C6 isotope.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol (vitamin D3) are the two form of vitamin D which are activated in vivo by hydroxylation. Vitamin D2 and D3 may be used in a wide range of studies to assess their effects on function such as immune function and calcium homeostasis.